You can read all the C# performance tips from the following links,
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part One - String Split
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part Two - String Equals
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part Three - Adding Strings
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part Four - List.Count() Vs List.Any()
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part Five - List.Count() Vs List.Count
- C# Programming Performance Tips - Part Six - Array Length
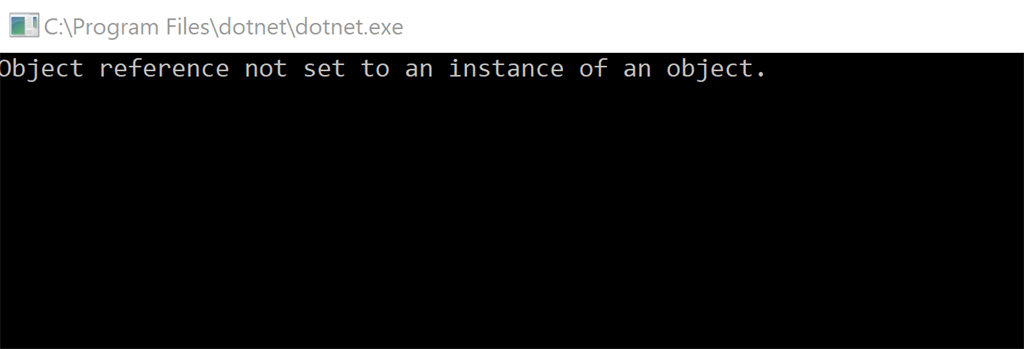
In the below code, we would like to check if the str variable's value is equal to the string “Akshay” or not. And, let us assume that somehow, we are getting the str variable value as null.
try {
string str = null;
if (str.Equals("Akshay")) {
Console.WriteLine("if");
} else {
Console.WriteLine("else");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
In this case, str.Equals will throw a null reference exception.
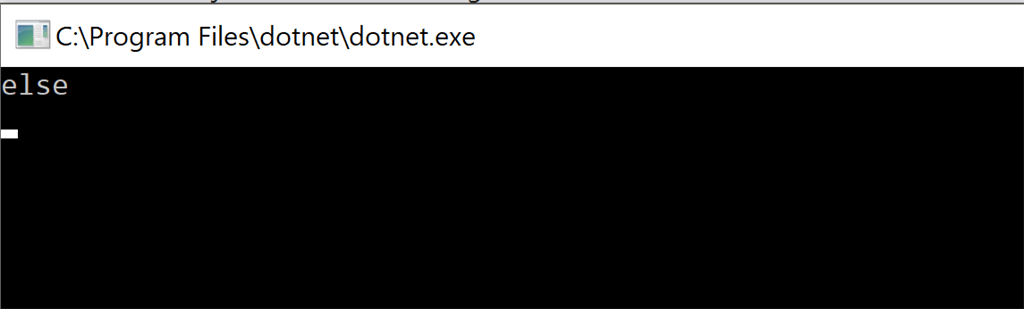
Now, let’s think in a little bit of a different way. Rather than using Equals method with str, let’s use it with our value, i.e., “Akshay”.
try {
string str = null;
if ("Akshay".Equals(str)) {
Console.WriteLine("if");
} else {
Console.WriteLine("else");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
In this case, the code will execute the else part instead of throwing a null reference exception.